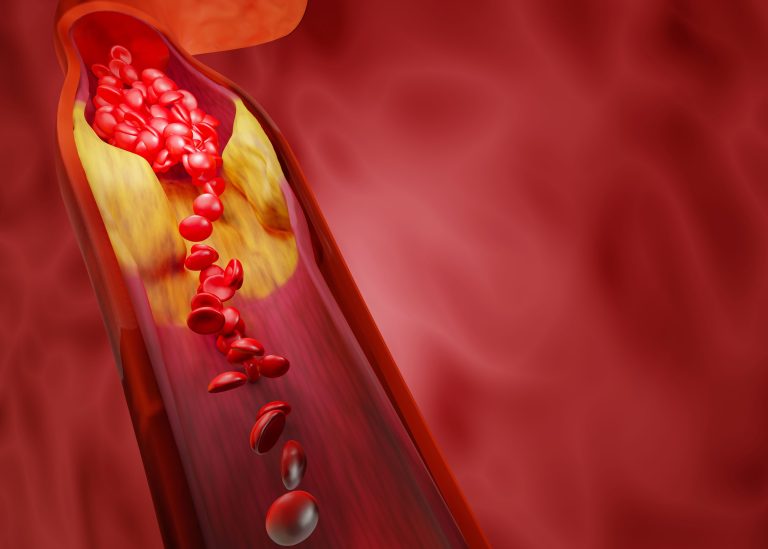
Hyperlipidemia, also known as high cholesterol, is a condition characterized by elevated levels of fats (lipids) in the blood. It is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. Understanding its causes, risks, and effective management is crucial for maintaining heart health.
Causes of Hyperlipidemia
Hyperlipidemia can result from various factors, including:
- Genetics: Family history plays a significant role in predisposing individuals to high cholesterol levels.
- Dietary habits: Consuming foods high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol contributes to elevated lipid levels.
- Lifestyle factors: Lack of physical activity, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption can raise cholesterol levels.
- Medical conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, obesity, and hypothyroidism can also affect lipid levels.
Risks Associated with Hyperlipidemia
Having high levels of lipids in the blood increases the risk of developing:
- Atherosclerosis: Build-up of plaque in arteries, leading to narrowing and potential blockages.
- Coronary artery disease: Reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, increasing the risk of heart attacks.
- Stroke: Reduced blood flow to the brain due to blockage or rupture of blood vessels.
- Peripheral artery disease: Narrowing of arteries in the legs, leading to decreased circulation and potential complications.
Symptoms of Hyperlipidemia
Hyperlipidemia itself usually does not cause symptoms. It is often diagnosed through routine blood tests measuring lipid levels, including total cholesterol, LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, and triglycerides.
Management of Hyperlipidemia
Effective management of hyperlipidemia focuses on:
- Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limiting saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol is crucial. Regular physical activity and smoking cessation are also recommended.
- Medications: When lifestyle changes alone are insufficient, medications such as statins, cholesterol absorption inhibitors, fibrates, or PCSK9 inhibitors may be prescribed to lower lipid levels.
- Regular monitoring: Periodic blood tests to monitor lipid levels and assess the effectiveness of treatment.
Preventing Hyperlipidemia
Preventative measures include:
- Healthy diet: Adopting a balanced diet low in saturated and trans fats, and rich in fiber and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Regular exercise: Engaging in physical activity most days of the week to help maintain a healthy weight and improve lipid profiles.
- Limiting alcohol intake: Moderating alcohol consumption to support heart health.
- Managing underlying conditions: Controlling diabetes, hypertension, and other medical conditions that can contribute to high lipid levels.
At IGAKU, we emphasize the importance of proactive management of hyperlipidemia to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Book a consultation today to receive personalized guidance and support for managing high cholesterol levels and maintaining heart health.
Ready to learn more about managing hyperlipidemia and improving your lipid profile? Book a consultation with IGAKU today. Our experts can provide comprehensive insights and tailored recommendations to help you achieve optimal cholesterol levels and reduce cardiovascular risks.
Read our other articles here.
- IGAKUhttps://igaku.co/blog/author/igaku/
- IGAKUhttps://igaku.co/blog/author/igaku/
- IGAKUhttps://igaku.co/blog/author/igaku/
- IGAKUhttps://igaku.co/blog/author/igaku/